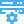
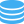
IPv4 - Subnetting made easy
Publisher: Psychz Networks, January 05,2015This How-to charts will help anyone seeking to know the Gateway, netmask, available IP address you can use on a specific IPV4 subnet.
Example: 23.238.0.8/29
- The CDIR chart tells me the netmask for this /29 is 255.255.255.248
- The /29 Subnet charts tell me that .8/29 gateway is .9 meaning that my gateway is 23.238.0.9
- The /29 Subnet chart has 10-14 as the vailable IP address for this /29, so 5 usable IP.
This chart removes the broadcast IP as it's not needed on a VLAN setup like ours. Howeve the last IP address + 1 would be the broadcast address. example 10-14 + 1 = 15 would be the broadcast address
CIDR chart
| CIDR | Addresses | Hosts | Netmask | Amount of Class C |
| /30 | 4 | 2 | 255.255.255.252 | 1/64 |
| /29 | 8 | 6 | 255.255.255.248 | 1/32 |
| /28 | 16 | 14 | 255.255.255.240 | 1/16 |
| /27 | 32 | 30 | 255.255.255.224 | 1/8 |
| /26 | 64 | 62 | 255.255.255.192 | 1/4 |
| /25 | 128 | 126 | 255.255.255.128 | 1/2 |
| /24 | 256 | 254 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 |
| /23 | 512 | 510 | 255.255.254.0 | 2 |
| /22 | 1024 | 1022 | 255.255.252.0 | 4 |
| /21 | 2048 | 2046 | 255.255.248.0 | 8 |
| /20 | 4096 | 4094 | 255.255.240.0 | 16 |
| /19 | 8192 | 8190 | 255.255.224.0 | 32 |
| /18 | 16384 | 16382 | 255.255.192.0 | 64 |
| /17 | 32768 | 32766 | 255.255.128.0 | 128 |
| /16 | 65536 | 65534 | 255.255.0.0 | 256 |
/25 Subnet -- 126 Hosts
Network Gateway Host
| 0 | 1 | 2-126 |
| 128 | 129 | 130-254 |
/26 Subnet -- 62 Hosts
Network Gateway Host
| .0 | .1 | .2-62 |
| .64 | .65 | .66-126 |
| .128 | .129 | .130.190 |
| .192 | .193 | .194-254 |
/27 Subnet -- 30 Hosts
Network Gateway Host
| 0 | 1 | 2-30 |
| 32 | 33 | 34-62 |
| 64 | 65 | 66-94 |
| 96 | 97 | 98-126 |
| 128 | 129 | 130-158 |
| 160 | 161 | 162-190 |
| 192 | 193 | 194-222 |
| 224 | 225 | 226-254 |
/28 Subnet -- 14 Hosts
Network Gateway Host
| 0 | 1 | 2-14 |
| 16 | 17 | 18-30 |
| 32 | 33 | 34-46 |
| 48 | 49 | 50-62 |
| 64 | 65 | 66-78 |
| 80 | 81 | 82-94 |
| 96 | 97 | 98-110 |
| 112 | 113 | 114-126 |
| 128 | 129 | 130-142 |
| 144 | 145 | 146-158 |
| 160 | 161 | 162-174 |
| 176 | 177 | 178-190 |
| 192 | 193 | 194-206 |
| 208 | 209 | 210-222 |
| 224 | 225 | 226-238 |
| 240 | 241 | 242-254 |
/29 Subnet-- 6 Hosts
Network Gateway Host
| 0 | 1 | 2-6 |
| 8 | 9 | 10-14 |
| 16 | 17 | 18-22 |
| 24 | 25 | 26-30 |
| 32 | 33 | 34-38 |
| 40 | 41 | 42-46 |
| 48 | 49 | 50-54 |
| 56 | 57 | 58-62 |
| 64 | 65 | 66-70 |
| 72 | 73 | 74-78 |
| 80 | 81 | 82-86 |
| 88 | 89 | 90-94 |
| 96 | 97 | 98-102 |
| 104 | 105 | 106-110 |
| 112 | 113 | 114-118 |
| 120 | 121 | 122-126 |
| 128 | 129 | 130-134 |
| 136 | 136 | 138-142 |
| 144 | 145 | 146-150 |
| 152 | 153 | 154-158 |
| 160 | 161 | 162-166 |
| 168 | 169 | 170-174 |
| 176 | 177 | 178-182 |
| 184 | 185 | 186-190 |
| 192 | 193 | 194-198 |
| 200 | 201 | 202-206 |
| 208 | 209 | 210-214 |
| 216 | 217 | 218-222 |
| 224 | 225 | 226-230 |
| 232 | 233 | 234-238 |
| 240 | 241 | 242-246 |
| 248 | 249 | 250-254 |