Quagga Routing - Install, Configure and setup BGP
Publisher: Psychz Networks, November 21,2017
Quagga routing suite is a fine open-source routing software. Quagga is a fork of GNU Zebra which allows the functionality of routing. Just like you can access router and give commands, you can do the same with this application.
Its architecture is very interesting since it is installed on Linux and it acts as an abstraction layer on the Kernel of Linux server and rest of the architecture consists of sockets on which all the communication occurs.
You can access all the protocols through CLI just like you are accessing some third layer router and you will not feel any difference in applying commands.
Quagga Installation
To install Quagga on your system, please use the following commands.
1. For CentOS operating system: yum install quagga
2. CentOS 7 operating system: yum install quagga setsebool zebra_write_config 1
3. Debian/Ubuntu family: apt-get install quagga
Quagga Configuration
The Quagga suite contains several different pieces of software that work together to accomplish successful routing. For BGP routing, we are focusing primarily on two daemons, namely
Zebra- A core daemon that focuses on kernel interfaces and static routing.
BGPd- A BGP daemon
Zebra Configuration
Once installed, we need to configure everything. Let’s start with Zebra and configure logging with it.
(Note: "quagga-XXXXX" in the above line refers to the version of Quagga that you have installed. For instance, we have installed version "quagga-0.99.22.4" in this case.)

chkconfig zebra on
systemctl enable zebra
Vtysh CLI
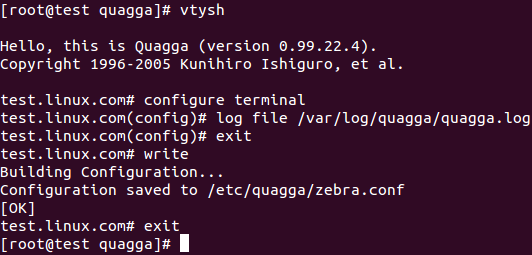
Quagga offers a dedicated CLI shell called vtysh. This CLI helps the user to interact with the software with user-friendly commands.
To launch vtysh, we use the following command.
Specify the log file for Zebra via the following command.
log file /var/log/quagga/quagga.log
exit
Now we save the configuration before exiting.
BGP peering Configuration
For BGP peering, we first copy the sample configuration file from "/usr/share/doc" to "/etc". Then, we will start and enable the bgp service. After all this is done, we configure the BGP session.
1) Let’s prepare the BGP daemon (BGPd)’s configuration file.
2) Start and enable the bgpd daemon
chkconfig bgpd on
systemctl enable bgpd
Now we enter the Quagga shell with the help of the following command.
Now let’s make our own BGP session.
router bgp <asn>
no auto-summary
no synchronization
neighbor <neighbor IP> remote-as <remote ASN>
neighbor <neighbor IP> description “Remote ASN”
exit
exit
write
Now please confirm that BGP is setup properly with the following command.
Configure prefix advertisements
In this example, we will advertise prefix 8.8.8.0/24. You can choose any prefix as per your network preferences.
router bgp <asn>
network 8.8.8.8/24
exit
write